Jun. 19, 2025
Uncertainty surrounding the Trump administration's tariff policy is directly and indirectly affecting the global economy and hindering stable growth. Even if extreme escalation is avoided, assuming the application of a 10% base tariff plus additional rates to many countries and the imposition of approximately 25% tariffs on specific products for the purpose of maintaining economic security, it is likely that the global economic growth rate for 2025–2026 will fall below 3%. Caution is also warranted regarding the resurgence of selling U.S. assets and the expansion of China's excess supply. The global real GDP growth rate is projected to be 2.8% in 2025 and 2.8% in 2026.
The U.S. economy is slowing. The Trump administration's broad implementation of tariffs will increase uncertainty about the outlook and is expected to put downward pressure on the U.S. economy in 2025. On the other hand, the tax cut bill currently under consideration will support the U.S. economy, especially in 2026. We expect the tariffs to temporarily increase inflation, but the impact will be limited; the Federal Reserve is expected to resume interest rate cuts in the second half of 2025 after assessing the impact of tariffs on prices. The risks are a sell-off in the U.S. and stalling consumption due to the Trump administration's policies, including higher interest rates due to fiscal concerns and a sharp drop in stock prices as tariff negotiations run into difficulties. Real GDP growth in the U.S. is projected to be 1.8% in 2025 and 1.6% in 2026.
The eurozone's real GDP growth rate accelerated in the January-March quarter of 2025. This was largely due to a surge in demand ahead of US tariff impositions and is expected to be temporary. The eurozone economy is projected to stagnate in the second half of 2025. On the other hand, increased defense spending and increased investment in infrastructure are expected to support the economy in 2026. The ECB is expected to cut its policy interest rate to just under 2% and keep it unchanged. The UK economy is expected to see stagnant consumption due to residual inflation, and the Bank of England is expected to implement gradual interest rate cuts. The eurozone's real GDP growth rate is projected to be 1.0% in 2025 and 0.8% in 2026. The UK's real GDP growth rate is projected to be 1.1% in 2025 and 1.0% in 2026.
The Chinese economy is weakening as business confidence deteriorates, especially in the manufacturing sector. Exports are expected to decline from 2024 levels due to the Trump tariffs, which will not be compensated by an increase in exports to Asia and other markets. The government decided on a policy of fiscal expansion at the National People's Congress, and manufacturing and infrastructure investment are expected to remain strong. On the other hand, corporate profits have been squeezed by falling prices for EVs and other products due to intensifying domestic competition, and exports of excess production at low prices are expected to continue. Consumption has been accelerating due to the expansion of measures to promote replacement purchases, but a large increase is unlikely due to asset deflation caused by stagnation in the real estate market and concerns about employment and income. Real GDP growth is forecast to be 3.9% in 2025 and 3.9% in 2026.
The Japanese economy has been stagnant due to high prices, especially for food, which have worsened consumer sentiment. However, real wages are expected to turn positive due to continued wage increases. With energy subsidies, consumption will recover in the second half of the year. Capital investment will continue to grow on the back of high profit margins and a sense of equipment shortages, but will slow, especially in the manufacturing sector, due to the Trump tariffs. Exports will decline YoY due to lower exports to the U.S. and weaker exports to China. Depending on negotiations with the U.S., there is a risk of downward pressure on manufacturing, especially in the auto sector. We expect the BOJ's additional interest rate hike to be delayed to 2026. Real GDP growth rate is forecast to be 0.8% (FY 0.5%) in 2025 and 0.6% (FY 0.6%) in 2026.
India continues to see stable inflation amid sustained resilience in corporate sentiment and consumer confidence, prompting the Central Bank to maintain its interest rate cuts. Going forward, while caution is needed regarding the potential negative impact on exports and business sentiment due to changes in the situation surrounding Trump tariffs, fiscal policies such as income tax cuts and accommodative monetary policies are expected to support private demand. Growth is forecast to be 6.1% for the 2025 fiscal year and 6.2% for the 2026 fiscal year. ASEAN-5 is also expected to continue to see stable growth overall, but there is a risk of negative impacts due to tariffs, China's economic slowdown and China's expansion of excess supply. The ASEAN-5's real GDP growth rate is expected to slow slightly from 5.0% in 2024 to 4.5% in 2025 and 4.4% in 2026, with growth projected to be around the mid-4% range.
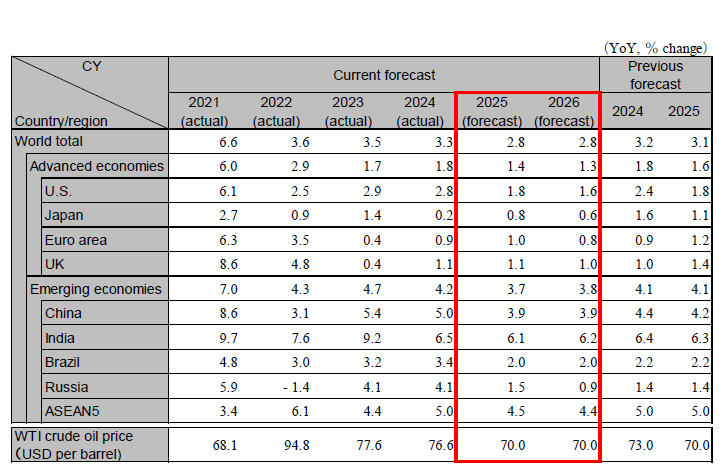
Note: Values for Japan differ from those shown in the table below on a fiscal-year basis because they are on a calendar-year basis. However, India’s figures are shown on a fiscal-year basis. ASEAN5 is comprised of Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Vietnam.
Source: Actual figures are from the IMF, forecasts are from the IMF (Brazil and Russia), and Hitachi Research Institute (others)
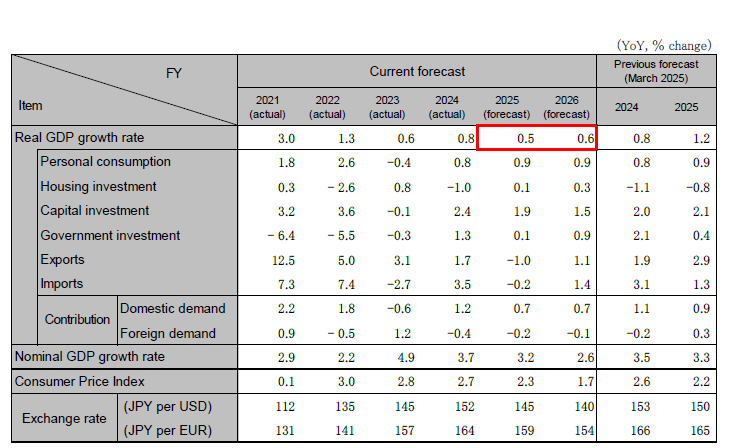
Note: The individual numbers and their sum may not match due to fractional processing.
Source: Cabinet Office, forecasts by Hitachi Research Institute
We provide you with the latest information on HRI‘s periodicals, such as our journal and economic forecasts, as well as reports, interviews, columns, and other information based on our research activities.
Hitachi Research Institute welcomes questions, consultations, and inquiries related to articles published in the "Hitachi Souken" Journal through our contact form.