Latest economic forecasts for Japan, the U.S., Europe, and China, etc
Global economy stalling after slowdown in 2023, full recovery delayed to 2024
The global economy in 2023 will stagnate mainly in the first half of the year due to the cumulative effect of interest rate hikes in various countries in 2022 and sluggish activity in China. Energy and minerals prices will peak out due to the global economic slowdown, and inflationary pressures will gradually ease. The tightening cycle aimed at curbing inflation will be completed by mid-year, and economies will enter a phase of waiting for a recovery, but growth will remain weak in the absence of an economic driving force, and a full recovery will be delayed to 2024. Global growth will be 3.3% in 2022 and 2.4% in 2023.
The U.S. economy will continue to decelerate, especially domestic demand, affected by higher interest rates and prices. Housing market conditions have deteriorated markedly, putting downward pressure on consumer spending and housing investment. Inflation is expected to halt its rise and to gradually decline toward the end of 2023. The FRB is expected to ease the pace of interest rate hikes, with a policy rate expected to rise to the low-5% range in the first half of 2023 before remaining unchanged. The FRB’s rate hikes will keep the U.S. economic growth rate almost flat in 2023. Real GDP growth is forecasted at 1.8% in 2022 and 0.3% in 2023.
The Euro area economy avoided entering a winter recession due to natural gas shortages, but business activity stagnated, and consumer spending remained sluggish due to rising electricity prices. The inflation rate will remain high in 2023, and stagflation will continue. In Germany, particularly, production will continue to decline, especially in the materials industry, as electricity prices rise. Household purchasing power will also decline, and the economy fell into recession from the end of 2022. The U.K. has also entered into a recession due to high inflation, rapid interest rate hikes, and austerity measures by the new government. Real GDP growth in the Euro area is forecasted at 3.3% in 2022 and 0.3% in 2023. Real GDP growth in the U.K. is forecasted to be 4.3% in 2022 and -0.8% in 2023.
In China, growth picked up after the Shanghai lockdown, but economic activity was disrupted by a resurgence of infections beginning in fall 2022, Economic growth will remain sluggish in late 2022 and early 2023 due to the slowdown in activity caused by the increase in COVID infections and weak consumer confidence. The real estate market will remain stagnant for the time being, as the recent supportive measures implemented lack an immediate effect. Improvement in both the consumption and real estate markets will not be confirmed until mid-2023. Growth is forecasted at 3.2% in 2022 and 4.6% in 2023.
India is expected to continue raising interest rates to control inflation until spring 2023. Although the economy will not stall, the cumulative effect of interest rate hikes plus slowing external demand will weigh on growth in 2023. Inflation will return to within the inflation target range (upper 6%) in the second half of 2023. Growth is expected to be 7.1% in FY2022 and 5.8% in FY2023. ASEAN economies will generally recover steadily, but inflation-curbing interest rate hikes will continue until mid-2023. The risk is the spillover effect of reduced overseas demand due to the economic slowdown in the U.S. and China. ASEAN5 growth is forecasted to be 5.7% in 2022 and 4.6% in 2023.
The recent sharp rise in crude oil and raw materials prices and the rapid depreciation of the yen have increased the value of imports and have continued the outflow of income overseas. Economic measures formulated by the government are expected to support the economy through curbing household electricity and gas price hikes from the beginning of 2023. Household savings are accumulating due to benefits and fewer opportunities to go out, and consumption will continue to recover as pent-up demand will emerge as crude oil and raw materials prices settle down as the overseas economic stagnates and the yen reverses from its depreciation. Capital investment is expected to recover due to improved corporate earnings, but the pace of recovery will be slow, due in part to deteriorating business conditions in the manufacturing sector because of declining exports. Economic growth will continue to recover at a moderate pace. Real GDP growth is forecasted to be 1.6% in FY2022 (1.2% in CY2022) and 1.1% in FY2023 (1.5% in CY2023).
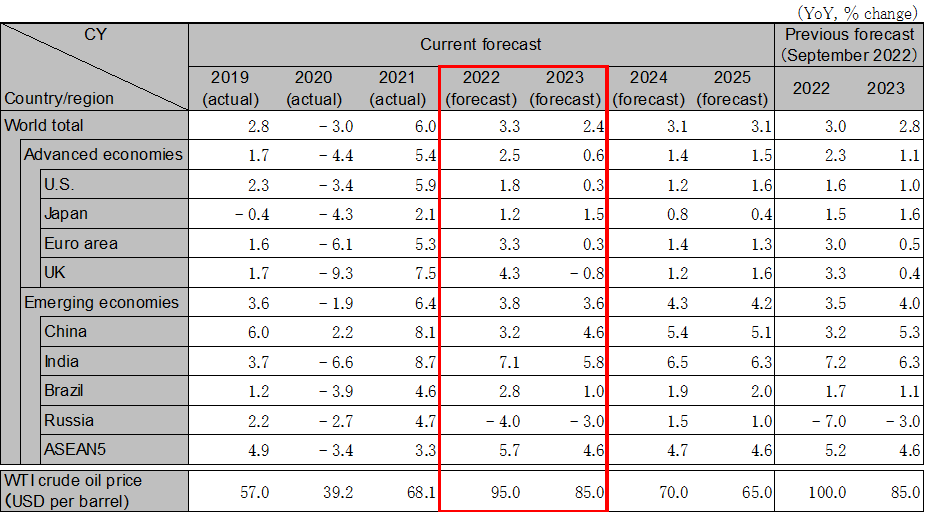
Note: The figures above are calendar-year based. Accordingly, the figures of Japan are different from the fiscal-year based figures in the table below.
Source: IMF. Forecast by Hitachi Research Institute.
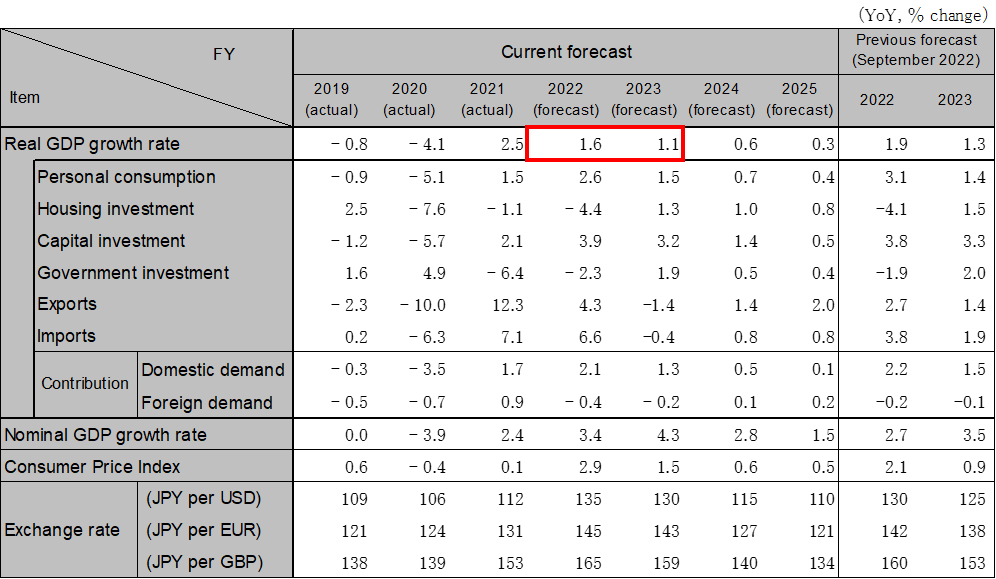
Source: Japan Cabinet Office, etc. Forecast by Hitachi Research Institute.