Latest economic forecasts for Japan, the U.S., Europe, and China, etc
Caution is needed during the second half of 2023 and the first half of 2024. Risks of a financial crisis and inflation must be watched out for.
The global economy has stalled somewhat due to the recovery of the service sector and the slowdown of the manufacturing sector. Inflation is still at a high level, so caution is still needed. The main scenario is a soft landing, although an economic slowdown is expected to intensify during the second half of 2023 due to the cumulative effects of interest rate hikes and lingering financial instability. In 2024, the recovery will accelerate starting in the second half of the year on the back of stabilized inflation and monetary easing in the US. Global GDP growth will be 2.7% in 2023 and 3.0% in 2024. Continued caution is needed with regard to the worsening financial crisis, longer-than-expected inflation, and interest rate hikes.
While the U.S. economy slowed down at the beginning of 2023 due to repeated interest rate hikes, the pace of the slowdown remained moderate. However, the U.S. economy is likely to slow down during the second half of 2023 amid rising credit concerns triggered by the failure of a medium-sized bank in March 2023, in addition to the Fed's continued rate hikes. Inflation, which has remained high mainly in the realm of service prices, is expected to gradually decline toward the end of 2023. The Fed is also expected to raise interest rates by an additional 0.5% through to September before starting to cut rates in March 2024. Real GDP growth rates are going to be 1.2% in 2023 and 0.7% in 2024.
The Euro area economy was contracted at an annual rate of -0.4% in the first quarter of 2023, the second consecutive quarter of negative growth. Production was sluggish in Germany and other major countries due to high industrial electricity prices. The ECB is expected to raise policy rates to the low 4% range in 2023 as the core inflation rate shows no signs of falling due to high food and service prices. Although the U.K. economy maintained positive growth at the beginning of 2023, the decline in purchasing power due to high inflation is likely to depress the growth rate during the second half of 2023. Real GDP growth in the Euro area will be 0.6% in 2023 and 1.4% in 2024. Real GDP growth in the U.K. will be 0.0% in 2023 and 0.9% in 2024.
China's growth is accelerating due to its COVID-19 policy shift. With an increase of the mobility of its people, business conditions in the service sector have improved. On the other hand, the unemployment rate among young people is rising. Improvement in consumer confidence remains limited amid job insecurity, and the recovery been seen in terms of consumption is moderate. Real estate investment has bottomed out, but the pace of recovery is slow. Market stagnation is expected to continue for the time being. The recovery in terms of consumption and real estate is expected to take place during the second half of 2023. Exports will remain sluggish but are expected to pick up in the second half of the year (mainly for items going to emerging countries such as ASEAN). Real GDP growth is projected to be 5.2% in 2023 and 5.4% in 2024.
In India, the rapid post-COVID consumption recovery is experiencing a pause, but business activity remains firm. Inflation is gradually stabilizing, and the Reserve Bank of India suspended interest rate hikes in April. Looking ahead, we are concerned about a decline in service exports due to an overseas slowdown, the cumulative effects of interest rate hikes, and a decline in agricultural production due to unfavorable weather conditions, etc. ASEAN economies are generally continuing to recover, but the pace of growth is gradually slowing. Inflation is showing signs of having gone past the peak, but there is currently a mixture of different monetary policies being implemented in each country. Going forward, caution is needed in relation to downward pressure on domestic demand due to higher interest rates and in relation to downward pressure on exports due to slowdowns in the U.S. and Europe. Real GDP Growth for ASEAN5 is projected to be 4.7% in 2023 and 5.0% in 2024.
Consumption is firm and generally approaching pre-COVID levels on the back of a recovery in people going out and an increase in inbound travelers. However, a pickup in real wages is needed to sustain consumption recovery and accelerate the pace of expansion. The BOJ is cautious about revising its policies to achieve price targets with wage growth. The revision or elimination of yield curve controls are not expected until 2024. Capital investment remains firm after the sharp recovery seen after the COVID-19 pandemic due to a recovery in production and higher profit margins seen in non-manufacturing sectors. Exports are expected to decline in FY2023 due to a global economic slowdown and are expected to recover in FY2024. Real GDP growth is projected to be 0.8% in FY2023 (1.0% in CY2023) and 1.2% in FY2024 (1.2% in CY2024).
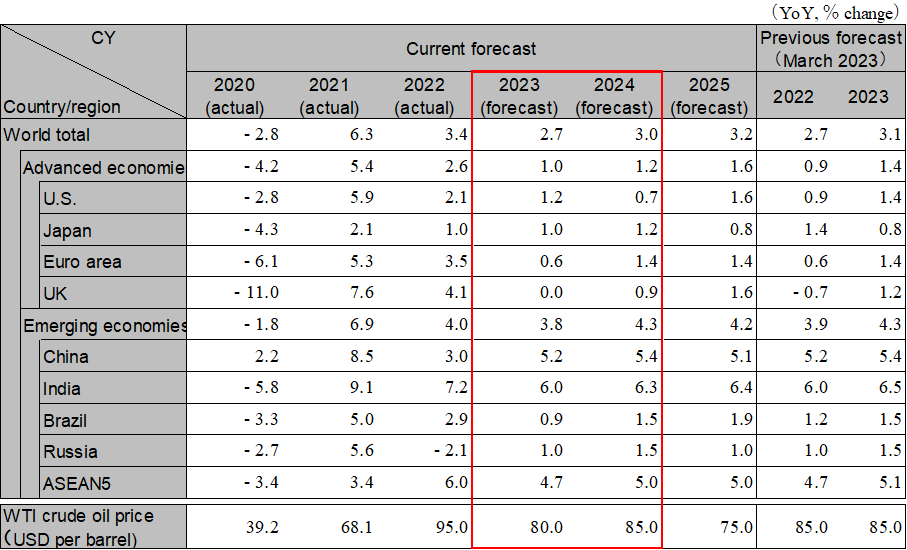
Note: The figures above are calendar-year based. Accordingly, the figures of Japan are different from the fiscal-year based figures in the table below.
Source: IMF. Forecast by Hitachi Research Institute.
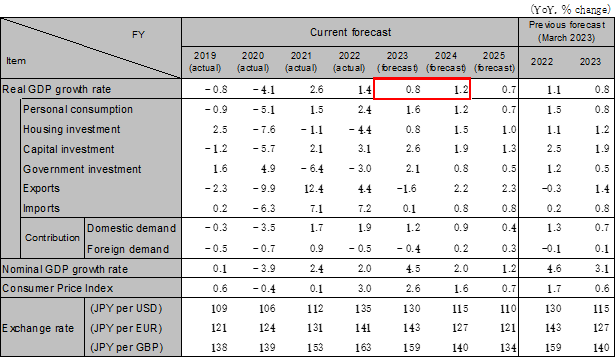
Source: Japan Cabinet Office, etc. Forecast by Hitachi Research Institute.